Gross anatomy[edit]
The adult human brain weighs on average about 1.2–1.4 kg (2.6–3.1 lb), or about 2% of the total body weight,[7][8] with a volume of around 1260 cm3 in men and 1130 cm3 in women, although there is substantial individual variation.[9]Neurological differences between the sexes have not been shown to correlate in any simple way with IQ or other measures of cognitive performance.[10]
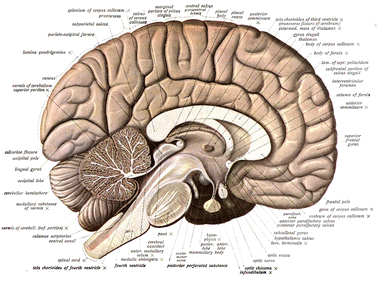
The cerebrum, consisting of the cerebral hemispheres, forms the largest part of the brain and is situated above the other brain structures.[11] The outer region of the hemispheres, the cerebral cortex, is grey matter, consisting of cortical layers. Each hemisphere is divided into four main lobes.[12]
The brainstem, resembling a stalk, attaches to and leaves the cerebrum at the start of the midbrain area. The brainstem includes the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. Behind the brainstem is the cerebellum (Latin: little brain).[11] Its cortex is narrowly furrowed horizontally.[13]
The cerebrum, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord are covered by three membranes called meninges. The membranes are the tough dura mater; the middle arachnoid mater and the more delicate inner pia mater. Between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater is the subarachnoid space, which contains the cerebrospinal fluid.[14] In the cerebral cortex, close to the basement membrane of the pia mater, is a limiting membrane called the glia limitans; this is the outermost layer of the cortex.[15] The living brain is very soft, having a gel-like consistency similar to soft tofu.[16] The neural layers of the cortex constitute much of the brain's grey matter, while the deeper subcortical regions of the brain, made up of myelinated axons, are the white matter.[11]

No comments:
Post a Comment